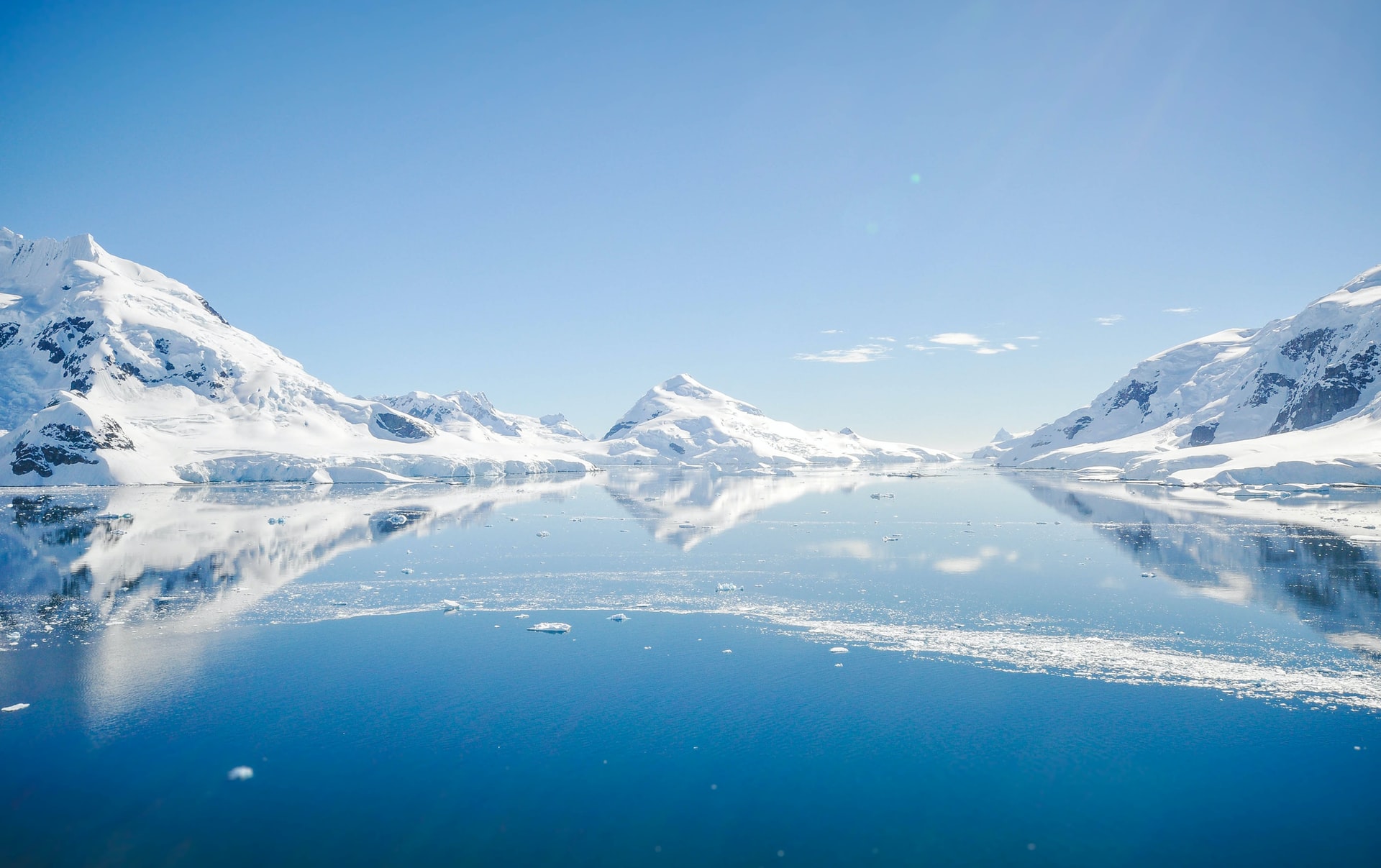
Antarctica’s circumpolar location and its isolation from other parts of the world determined the uniqueness and extreme severity of its natural conditions.
The main feature of Antarctica is the ice sheet, which exists for millions of years, now decreasing, now increasing in size.
Mainland ice covers both the surface of Antarctica and partially the surface of the ocean, forming ice shelves. The thickness of the ice sheet is 4000-4776 m. Its total volume is 90% of all modern glaciation of the Earth. Ice is constantly moving from the center to the edges at a rate of 1 m per year. At the same time the edges of the ice are cracking and icebergs are breaking away from it. Only 0.2% of Antarctica’s surface is ice-free.
The eastern part of the continent lies on the ancient Antarctic platform with a relatively flat surface, while the western part has mountainous terrain and is an extension of the Andes of South America. The highest point of the continent is located in the Vinson Mountains and has a height of 5140 m. In the western part there are active volcanoes – Erebus (3794 m), Terror and others. The average height of the continent above sea level (together with the ice) is 2040 g. The ice cover of Antarctica presses on the Earth’s crust, and it sagged under its weight (in some places even dropped below sea level). There are deposits of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, coal and diamonds on the continent.
The climate in Antarctica is very cold. On the mainland recorded the lowest temperatures on Earth (in winter – almost -90 ° C). The main reasons for this are: the geographical location of the continent, its thick ice cover (a constant source of cold, which also reflects the sun’s rays), the long polar night, the high altitude of the continent above sea level.
The air over Antarctica is cold, heavy, and dry, so an area of high atmospheric pressure forms in the center. At the margins, the neighborhood with relatively warm oceanic waters causes higher air temperatures and, as a consequence, the formation of an area of low atmospheric pressure. Therefore, air flows from the center to the margins, forming runoff winds (velocity 40-50 m/s and more).
On the continental margins and on the Antarctic Peninsula, oases are formed, which are characterized by dry and cold desert conditions. In summer, their surface warms up and becomes free of snow and ice.
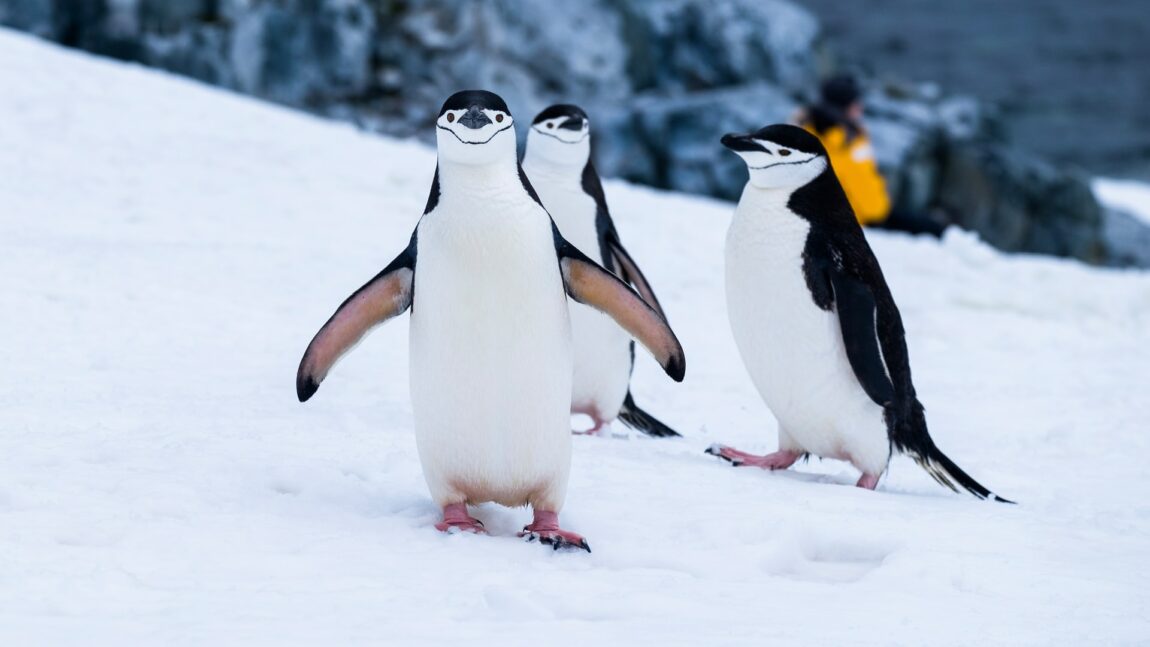

Antarctica is a biological desert. Vegetation is found exclusively on the fringes and on the sub-Antarctic islands. It is represented by mosses, lichens, algae and fungi. In the coastal waters there is a lot of plankton, which feeds on whales, seals and fish, most of which are endemics. Here live the most seals (sea elephants) and huge jellyfish weighing up to 150 kg. Of birds are characteristic penguins, in the summer arrive gulls, cormorants, petrels, skuas and albatrosses.
Active study of Antarctica is due to the great interest in the uniqueness of its nature. Antarctica is an active center of atmospheric circulation. Study of ice is important not only because they are the main resource of fresh water, but also an indicator of global warming. Mineral resources are also being studied.